自定义线程池
1.原理图
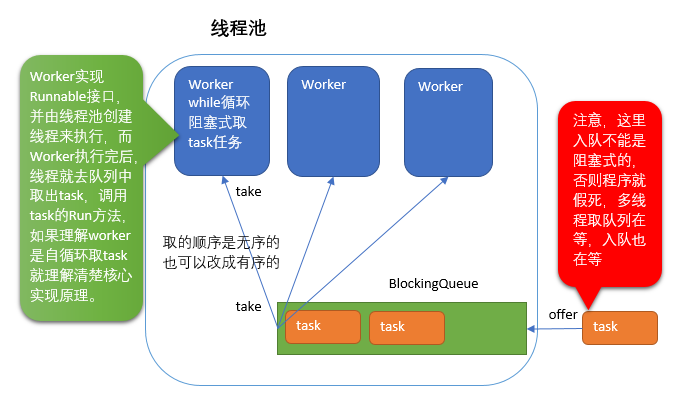
线程池构造的核心几个点
- 线程池里的核心线程数与最大线程数
- 线程池里真正工作的线程
worker - 线程池里用来存取任务的队列
BlockingQueue - 线程中的任务
task
这个Worker是个内部类,是在线程池内声明的。
exec方法

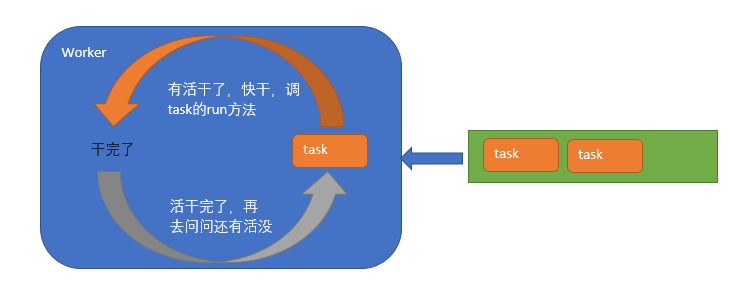
Worker怎么工作
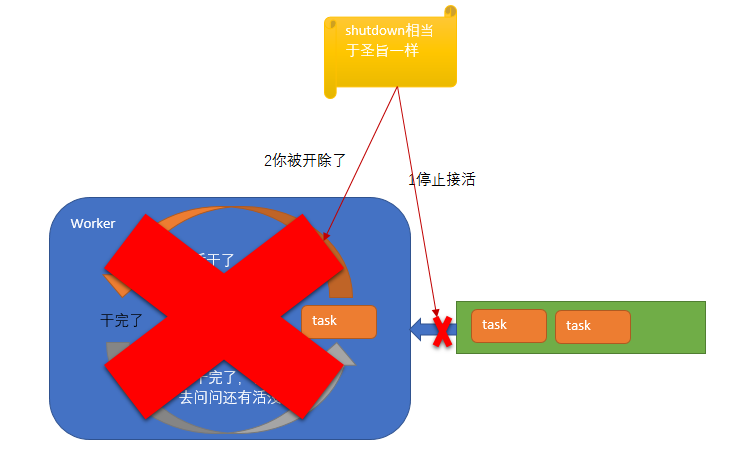
shutdown()
2.代码实现
package com.example.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
public class ThreadExcutor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadExcutor excutor = new ThreadExcutor(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
excutor.exec(() -> {
System.out.println("线程 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 在帮我干活");
});
}
}
//创建
private volatile boolean RUNNING = true;
//所有任务都放队列中,让工作线程来消费
private static BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = null;
private final HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet<Worker>();
private final List<Thread> threadList = new ArrayList<Thread>();
//工作线程数
int poolSize = 0;
//核心线程数(创建了多少个工作线程)
int coreSize = 0;
boolean shutdown = false;
public ThreadExcutor(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(poolSize);
}
public void exec(Runnable runnable) {
if (runnable == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (coreSize < poolSize) {
addThread(runnable);
} else {
//System.out.println("offer" + runnable.toString() + " " + queue.size());
try {
queue.put(runnable);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void addThread(Runnable runnable) {
coreSize++;
queue.offer(runnable);
Worker worker = new Worker();
workers.add(worker);
Thread t = new Thread(worker);
threadList.add(t);
try {
t.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void shutdown() {
RUNNING = false;
if (!workers.isEmpty()) {
for (Worker worker : workers) {
worker.interruptIfIdle();
}
}
shutdown = true;
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
/**
* 工作线程
*/
class Worker implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
while (RUNNING) {
if (shutdown) {
Thread.interrupted();
}
Runnable task = null;
try {
task = getTask();
task.run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public Runnable getTask() throws InterruptedException {
return queue.take();
}
public void interruptIfIdle() {
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " interrupt");
thread.interrupt();
}
}
}
}